-
Single-crystal EPR study and DFT structure of the [Mo(CO)5PPh3]+· radical cation
H. Sidorenkova, T. Berclaz, B. Ndiaye, A. Jouaiti and M. Geoffroy
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 70 (3-4) (2009), p713-718


DOI:10.1016/j.jpcs.2009.02.010 | unige:3549 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF
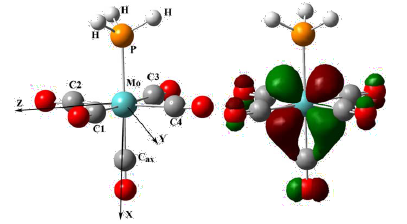
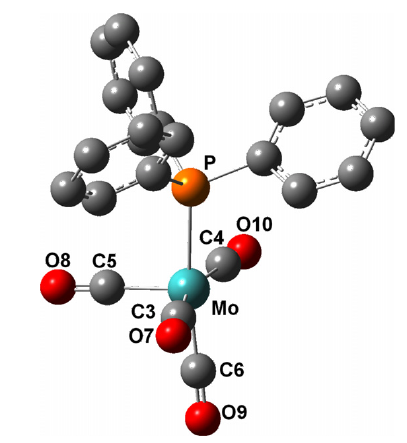
A radical species characterized by a large g-anisotropy and a clearly resolved hyperfine structure with 95/97Mo and 31P nuclei is formed, at 77 K, by radiolysis of a single crystal of Mo(CO)5PPh3. The corresponding EPR signals disappear irreversibly with increasing temperature and the angular dependence of the various coupling constants imply a spin delocalization of not, vert, ∼60% and not, vert, ∼4% on the molybdenum and the phosphorus atoms, respectively and are, a priori, consistent with the trapping of a one-electron deficient centre. The ability of DFT to predict the EPR tensors for a 17-electron Mo(I) species is verified by calculating the g-tensor and the various 14N and 13C coupling tensors previously reported by Hayes for [Mo(CN)5NO]3-. Calculations at the B3LYP/ZORA/SOMF level of theory show that, in contrast to Mo(CO)5PH3, one-electron oxidation of Mo(CO)5PPh3 causes an appreciable change in the geometry of the complex. The g-tensor and the 95/97Mo and 31P isotropic and anisotropic coupling constants calculated for [Mo(CO)5PPh3]+· confirm the trapping of this species in the irradiated crystal of Mo(CO)5PPh3; they also show that the conformational modifications induced by the electron release are probably hindered by the nearby complexes.